Overview of Bit Lightning
Cognitive Science & Solutions will release “Bit Lightning” technology this month!
This product is a revolutionary new technology inspired by our ground-breaking Elastic Representations™ approach to representing information within neural networks.
Artificial Intelligence is notorious for its insatiable demands for computing power and electricity. Enormous Data Centers are springing up all over the globe to support the computational demands of AI. The resulting costs, carbon footprint and impact on the environment are well known as critical concerns.
Bit Lightning technology can make an enormous difference!
Bit Lightning technology can slash the computational costs associated with AI!
What Does Bit Lightning Technology Do?
Abstract: Much of the computational load of AI is driven by expensive Vector Similarity searches employed by Retrieval Augmented Generation. Bit Lightning technology slashes those costs. Bit lightning can also slash the costs associated with recommendation systems and other popular number-crunching applications of vector databases.
A key part of today’s Generative Artificial Intelligence is RAG – Retrieval Augmented Generation. RAG employs enormous vector databases to store information that the AI can use to help understand queries and generate responses.
Vector databases are used for many applications besides RAG, such as recommendation systems, medicine and bioinformatics, fraud detection, computer vision, and advertising. These vector databases can contain Millions or Billions of vectors with hundreds or thousands of components in each vector. RAG technology, for example, converts an input query into a vector and then searches the vector database looking for the most similar vectors.
Computing the vector similarity search is extremely intensive, typically requiring the multiplication of each component in a vector with the corresponding component in the other vector, then adding all those products, just to measure the similarity between two vectors! Imagine the computational load to compare each input vector against the entire vector database!
Bit Lightning technology allows vector similarities to be computed lightning fast, slashing server and electrical costs. It can be applied not only to vectors with numeric data but also to categories, binary data and even text. The user can select their desired accuracy for entire vectors or tailor the accuracy of one vector component at a time. Bit Lightning computes a similarity metric which is linear in (absolute) distance and normalized, making it suitable for vectors with hundreds of dimensions.
Bit Lightning technology can slash computational load dramatically!!
Bit Lightning technology converts each vector in the database, and each of the incoming vectors, into a Lite Vector which is a good mathematical approximation of the original vector, but represented in a fundamentally unique way. We convert the vectors into a form which allows them to be rapidly compared, without multiplication, by using extremely efficient hardware that is a part of every computer. By eliminating multiplications and replacing that operation with something vastly more efficient, Bit Lightning technology can slash the computational costs associated with computing vector similarities!
How Efficient is Bit Lightning Technology?
As one would expect, the improved computational performance varies with the degree of accuracy required when converting the original, numeric vectors into Lite Vectors. Reducing the required accuracy results in faster, cheaper computations. The exact computational performance depends on many factors, including the type of computer, the exact code implementation, and the length of the vectors (number of dimensions).
In the plots below we compare Bit Lightning to the computation of the well-known cosine similarity using conventional numeric vectors as the input.
While Bit Lightning does not return a measure of cosine similarity, we do provide a new and powerful measure of the similarity between vectors. The resulting measure which can then be applied to numeric and non-numeric vector data, has a key strength of being normalized. Specifics on the Bit Lightning similarity metric are forthcoming.
What accuracy do we provide?
The user can select the accuracy they need. In some cases, they may require just 2 or 3 bits of accuracy. In other cases, they might require 6 or 7 bits of accuracy. The user can select the accuracy required, and determine where they want to be in the trade-off between execution speed and accuracy.
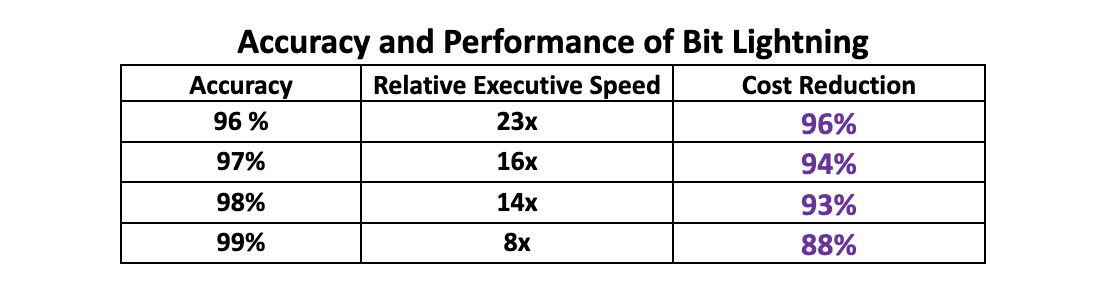
The table below presents some of our test results, where the relative execution speed compares the speed of computing the cosine similarity with numeric vectors to the computational speed achieved with our Bit Lightning technology.
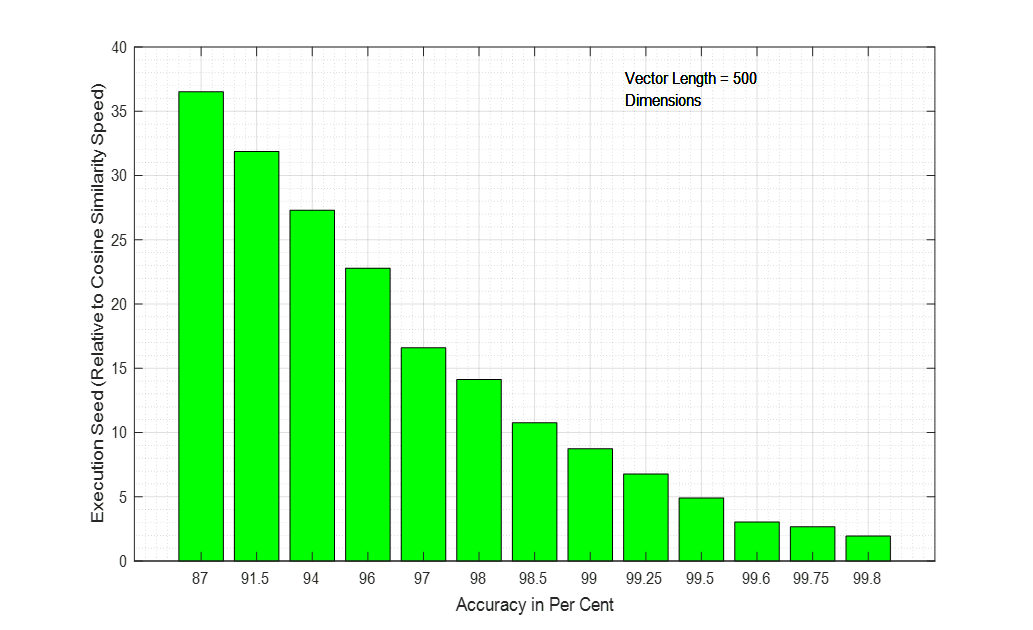
The plot below illustrates the execution speed of Bit Lightning compared to the execution speed of the cosine similarity, when tested on a laptop computer. The execution speed for Cosine Similarity appears as the green line. The Resolution in bits refers to the accuracy given by Bit Lightning, in terms of equivalent bits of accuracy (resolution).
The User Can Select the Accuracy Component by Component
We allow the user to select the accuracy they want, measured in bits of accuracy. They can decide to apply that accuracy across the entire vector or tailor the accuracy component by component. They can decide that some components do not warrant much accuracy while applying high levels of accuracy to the components that convey the most information. Furthermore, this technology allows the user to select the accuracy with Half-Bit resolution! In other words, they could decide that certain components are best handled with, for example, 4.5 bits of accuracy!
How to Use Bit Lightning Technology
Users can control Bit Lightning through our User Interface or via the Command Line Interface. The screenshots below show how the user interacts with the Bit Lightning User Interface to set up and run our technology.
Step 1: Select Vector Data Source
The user provides the path to access their vector file.
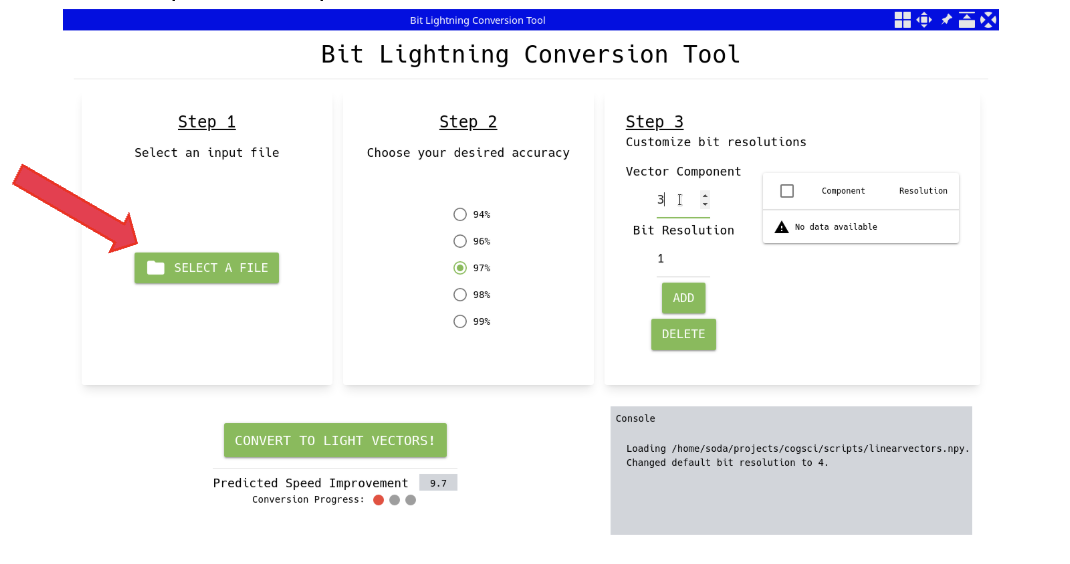
Step 2: Select Default Bit Accuracy for Entire Vectors
The UI displays a list of allowed bit accuracies, from 1 bit to 8 bits, in half-bit steps. The selected accuracy will be applied to All the vector components in the vector database as the default accuracy. The user selects the smallest default accuracy that makes sense, understanding that lower accuracies run faster, are more efficient, and cost less.
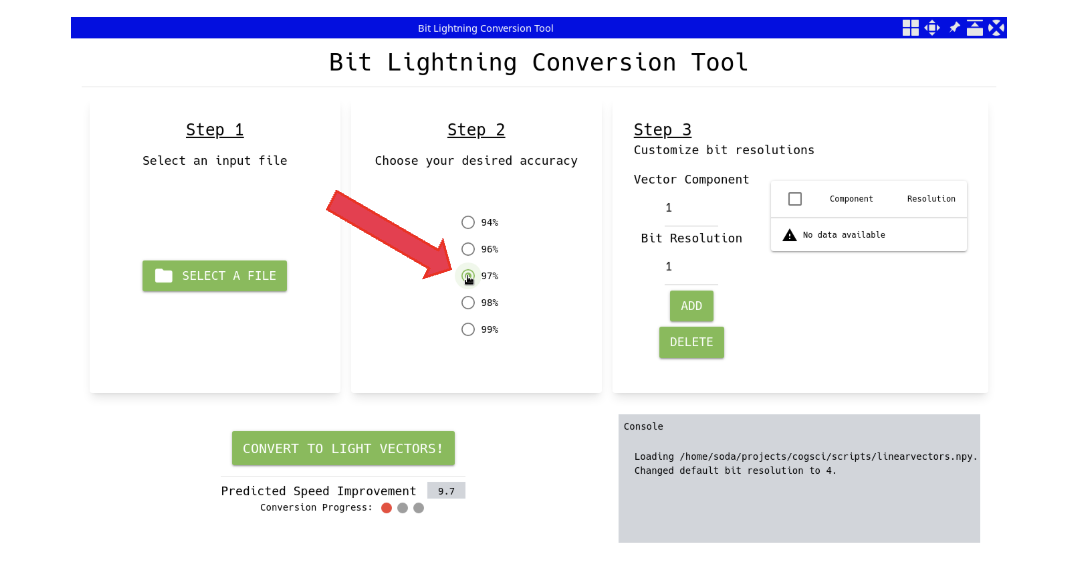
Step 3: Customize the Accuracy Component by Component
There may be some components where more accuracy is required or less accuracy is sufficient. The UI allows the user to navigate to those components and override the default bit accuracy with a customized value for that component.
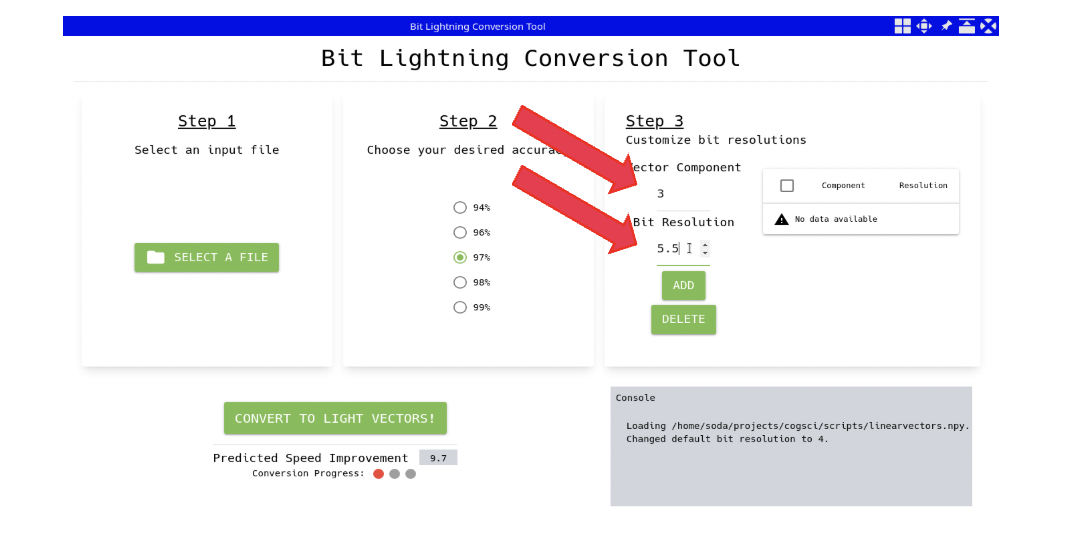
Next: The UI acknowledges the user’s input for customization….
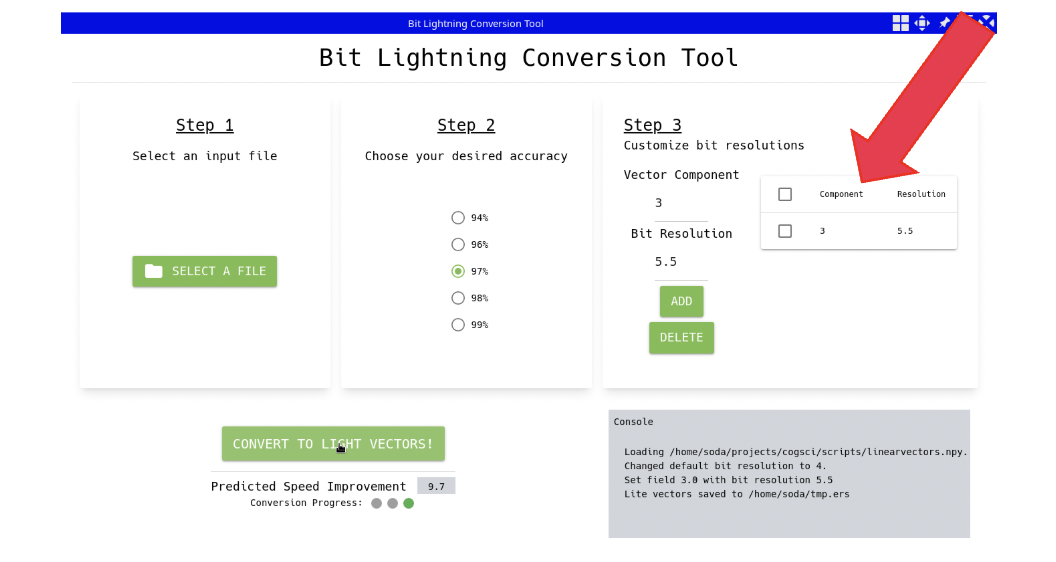
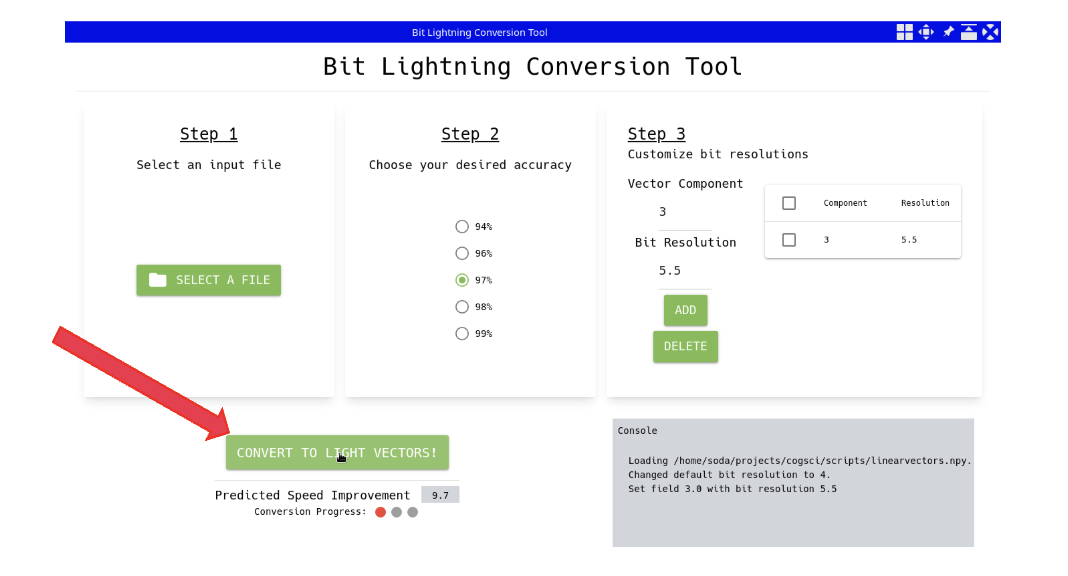
Step 4: CONVERT
When the user is done setting the accuracy required for their vector database, they hit “CONVERT.” The UI indicates that the software is busy converting the user’s vector database into Lite Vectors. When the Conversion is complete, the UI indicates “CONVERSION COMPLETED.”
Final Step: EXECUTE
When the conversion step is done, you are ready to compute the vector similarity, as follows:
- Convert your input vector to a Lite Vector, using the same bit accuracy parameters as before.
- Compute the vector similarity between the input Lite Vector and the Lite Vectors in your database, using the code we supply. We supply the code that does the hard work of computing vectors similarities without multiplications, using the computer’s more efficient machinery.
Bit Lightning is Available NOW!
Businesses that provide vector database services or perform large-scale computations of vector similarity are encouraged to contact us for more information or a free trial.


